Kawasaki Disease: Signs, Symptoms & Diagnosis
What are the symptoms?
Kawasaki disease (KD) is diagnosed when a patient runs a fever of 101°F – 104°F and above for at least five days. (If the fever isn’t treated, it can last up to 11 days.) The fever is accompanied by at least four of the following five symptoms:
- A rash over the torso, especially in the groin area.
- Redness and swelling of the palms and soles of the feet when the illness starts. Light peeling of the skin on the fingertips and toes occurs in the second and third weeks. Larger pieces of skin can peel off the hands and feet as well.
- Bloodshot eyes that can be sensitive to light.
- Swollen lymph glands in the neck (one large lymph node that measures more than 1.5 centimeters ). Sometimes the neck feels stiff.
- Irritation and inflammation of the mouth, lips and throat. “Strawberry” tongue – the tongue is bumpy and red with enlarged taste buds.
Patients may experience abdominal pain. About one-third develop temporary arthritis with pain and swelling of knee, hip and ankle joints. Incomplete Kawasaki disease should be considered if a child has fever and inflammation without all the symptoms above.
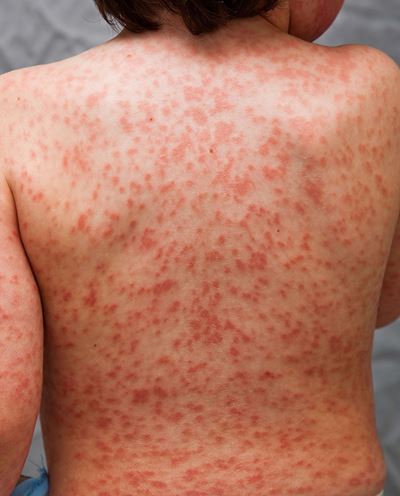
Photo courtesy of Kawasaki Disease Foundation
What causes it and how can it be prevented?
We aren’t sure what causes KD, but it doesn’t seem to be contagious. It’s also not hereditary in a typical way, although more than one child in a family can develop it, which may indicate a genetic predisposition.
There’s no known way to prevent KD. Parents should know that there’s nothing they could’ve done to prevent the disease.
How is KD diagnosed?
A health care provider must examine the child, observe signs and symptoms and rule out similar diseases. Just one test or even a group of tests by a health care provider won’t diagnose KD.
An echocardiogram will provide a baseline picture of the heart, even though a normal echocardiogram doesn’t always mean the child is free of KD. The health care provider may request blood tests or diagnostic studies.
Learn more:
Last Reviewed: Nov 19, 2019
