Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR): First aid
Cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is a lifesaving procedure that’s useful in a lot of emergencies, these kinds of as a heart assault or close to drowning, in which someone’s respiration or heartbeat has stopped. The American Heart Association suggests starting off CPR with difficult and fast chest compressions. This arms-only CPR suggestion applies to equally untrained bystanders and to start with responders.
If you’re afraid to do CPR or uncertain how to carry out CPR correctly, know that it is really always greater to try than to do practically nothing at all. The variance concerning executing anything and executing practically nothing could be someone’s lifestyle.
Here’s guidance from the American Heart Association:
- Untrained. If you’re not experienced in CPR or fearful about offering rescue breaths, then give arms-only CPR. That suggests uninterrupted chest compressions of a hundred to a hundred and twenty a moment right until paramedics arrive (described in far more detail beneath). You don’t require to try rescue respiration.
- Skilled and ready to go. If you’re effectively-experienced and self-confident in your ability, test to see if there is a pulse and respiration. If there is no pulse or respiration within just 10 seconds, start out chest compressions. Start off CPR with thirty chest compressions in advance of offering two rescue breaths.
- Skilled but rusty. If you have earlier obtained CPR schooling but you’re not self-confident in your qualities, then just do chest compressions at a level of a hundred to a hundred and twenty a moment (facts described beneath).
The higher than guidance applies to scenarios in which older people, children and infants require CPR, but not newborns (infants up to four weeks aged).
CPR can keep oxygen-loaded blood flowing to the brain and other organs right until crisis clinical treatment can restore a typical heart rhythm. When the heart stops, your system no for a longer time will get oxygen-loaded blood. The deficiency of oxygen-loaded blood can bring about brain damage in only a several minutes.
If you are untrained and have immediate access to a mobile phone, phone 911 or your local crisis amount in advance of beginning CPR. The dispatcher can instruct you in the suitable processes right until assistance arrives. To master CPR thoroughly, get an accredited to start with-help schooling study course, such as CPR and how to use an automated exterior defibrillator (AED).
Right before you start out
Right before starting off CPR, test:
- Is the environment secure for the particular person?
- Is the particular person conscious or unconscious?
- If the particular person appears unconscious, faucet or shake his or her shoulder and check with loudly, “Are you Alright?”
- If the particular person will not respond and you’re with a further particular person who can assistance, have a person particular person phone 911 or the local crisis amount and get the AED, if a person is offered. Have the other particular person start out CPR.
- If you are by itself and have immediate access to a telephone, phone 911 or your local crisis amount in advance of beginning CPR. Get the AED if a person is offered.
- As shortly as an AED is offered, provide a person shock if instructed by the unit, then start out CPR.
Recall to spell C-A-B
Upper body compressions
Upper body compressions
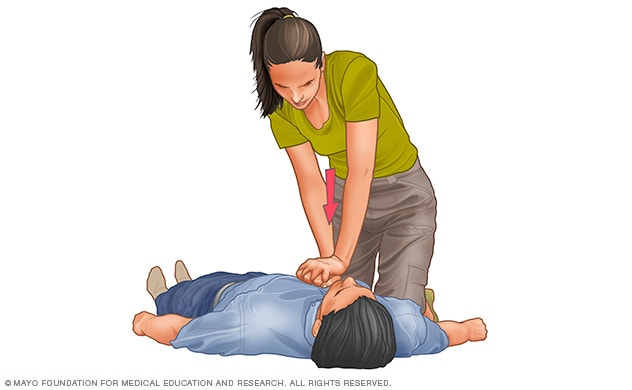
Upper body compressions
To carry out chest compressions, kneel up coming to the person’s neck and shoulders. Put the heel of a person hand about the heart of the person’s chest and your other hand on leading of the to start with hand. Maintain your elbows straight and posture your shoulders immediately higher than your arms. Making use of your upper system excess weight, press straight down on the chest about two inches (five centimeters), but not far more than two.four inches (six centimeters). Press difficult at a level of a hundred to a hundred and twenty compressions a moment. If you haven’t been experienced in CPR, continue chest compressions right until there are symptoms of motion or right until crisis clinical staff get about. If you have been experienced in CPR, go on to opening the airway and rescue respiration.
Open the airway
Open the airway
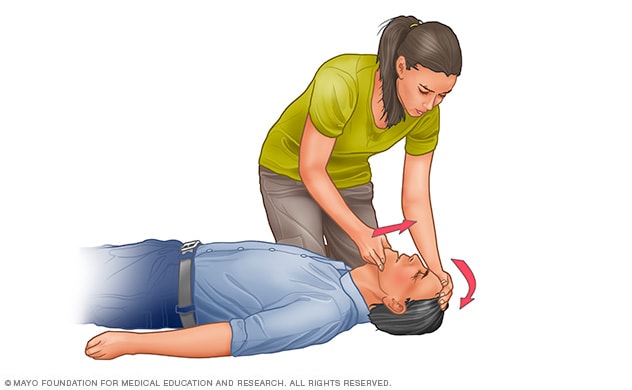
Open the airway
If you’re experienced in CPR and you have done thirty chest compressions, open up the person’s airway using the head-tilt, chin-elevate maneuver. Put your palm on the person’s forehead and gently tilt the head back. Then with the other hand, gently elevate the chin ahead to open up the airway.
Rescue respiration
Rescue respiration
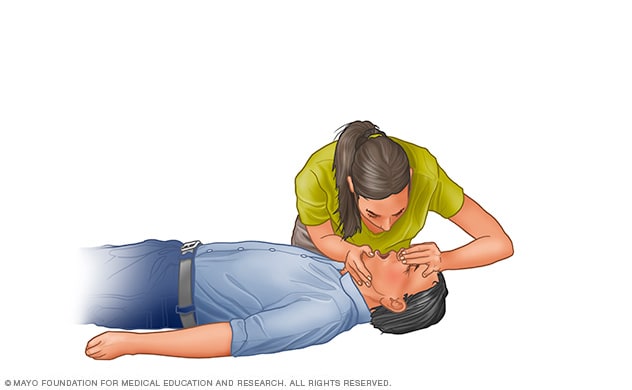
Rescue respiration
Open the airway using the head-tilt, chin-elevate maneuver. Pinch the nostrils shut for mouth-to-mouth respiration and address the person’s mouth with yours, generating a seal. Give the to start with rescue breath, lasting a person second, and enjoy to see if the chest rises. If it rises, give the second breath. If the chest will not rise, repeat the head-tilt, chin-elevate maneuver to start with and then give the second breath. Be careful not to give way too a lot of breaths or to breathe with way too much drive. Following two breaths, straight away restart chest compressions to restore blood stream.
The American Heart Association makes use of the letters C-A-B to assistance individuals don’t forget the buy to carry out the actions of CPR.
- C: compressions
- A: airway
- B: respiration
Compressions: Restore blood stream
Compressions suggests you can expect to use your arms to press down difficult and fast in a distinct way on the person’s chest. Compressions are the most significant phase in CPR. Observe these actions for performing CPR compressions:
- Put the particular person on his or her back on a agency floor.
- Kneel up coming to the person’s neck and shoulders.
- Put the lessen palm (heel) of your hand about the heart of the person’s chest, concerning the nipples.
- Put your other hand on leading of the to start with hand. Maintain your elbows straight and posture your shoulders immediately higher than your arms.
- Press straight down on (compress) the chest at least two inches (five centimeters) but no far more than two.four inches (six centimeters). Use your total system excess weight (not just your arms) when executing compressions.
- Press difficult at a level of a hundred to a hundred and twenty compressions a moment. The American Heart Association indicates performing compressions to the beat of the music “Stayin’ Alive.” Allow the chest to spring back (recoil) just after every press.
- If you haven’t been experienced in CPR, continue chest compressions right until there are symptoms of motion or right until crisis clinical staff get about. If you have been experienced in CPR, go on to opening the airway and rescue respiration.
Airway: Open the airway
If you’re experienced in CPR and you have done thirty chest compressions, open up the person’s airway using the head-tilt, chin-elevate maneuver. Put your palm on the person’s forehead and gently tilt the head back. Then with the other hand, gently elevate the chin ahead to open up the airway.
Respiration: Breathe for the particular person
Rescue respiration can be mouth-to-mouth respiration or mouth-to-nose respiration if the mouth is critically wounded or can not be opened. Recent recommendations suggest performing rescue respiration using a bag-mask unit with a higher-effectiveness particulate air (HEPA) filter.
- Following opening the airway (using the head-tilt, chin-elevate maneuver), pinch the nostrils shut for mouth-to-mouth respiration and address the person’s mouth with yours, generating a seal.
- Prepare to give two rescue breaths. Give the to start with rescue breath — lasting a person second — and enjoy to see if the chest rises.
- If the chest rises, give a second breath.
- If the chest will not rise, repeat the head-tilt, chin-elevate maneuver and then give a second breath. 30 chest compressions followed by two rescue breaths is viewed as a person cycle. Be careful not to give way too a lot of breaths or to breathe with way too much drive.
- Resume chest compressions to restore blood stream.
- As shortly as an automated exterior defibrillator (AED) is offered, use it and adhere to the prompts. Give a person shock, then resume chest compressions for two far more minutes in advance of offering a second shock. If you’re not experienced to use an AED, a 911 operator or a further crisis clinical operator could be capable to give you guidelines. If an AED just isn’t offered, go to phase five beneath.
- Go on CPR right until there are symptoms of motion or crisis clinical staff get about.
To carry out CPR on a kid
The method for offering CPR to a kid age 1 by means of puberty is effectively the very same as that for an adult — adhere to the C-A-B actions. The American Heart Association states you should really not hold off CPR and delivers this guidance on how to carry out CPR on a kid:
Compressions: Restore blood stream
If you are by itself and didn’t see the kid collapse, commence chest compressions for about two minutes. Then immediately phone 911 or your local crisis amount and get the AED if a person is offered.
If you’re by itself and you did see the kid collapse, phone 911 or your local crisis amount to start with. Then get the AED, if offered, and commence CPR. If a further particular person is with you, have that particular person phone for assistance and get the AED even though you commence CPR.
- Put the kid on his or her back on a agency floor.
- Kneel up coming to the child’s neck and shoulders.
- Put two arms (or only a person hand if the kid is extremely compact) on the lessen 50 % of the child’s breastbone (sternum).
- Making use of the heel of a person or equally arms, press straight down on (compress) the chest about two inches (close to five centimeters) but not larger than two.four inches (close to six centimeters). Press difficult and fast — a hundred to a hundred and twenty compressions a moment.
- If you haven’t been experienced in CPR, continue chest compressions right until the kid moves or right until crisis clinical staff get about. If you have been experienced in CPR, open up the airway and commence rescue respiration.
Airway: Open the airway
If you’re experienced in CPR and you have done thirty chest compressions, open up the child’s airway using the head-tilt, chin-elevate maneuver.
- Put your palm on the child’s forehead and gently tilt his or her head back.
- With the other hand, gently elevate the chin ahead to open up the airway.
Respiration: Breathe for the kid
Observe these actions for mouth-to-mouth respiration for a kid.
- Following using the head-tilt, chin-elevate maneuver to open up the airway, pinch the child’s nostrils shut. Go over the child’s mouth with yours, generating a seal.
- Breathe into the child’s mouth for a person second and enjoy to see if the chest rises. If it rises, give a second breath. If the chest will not rise, repeat the head-tilt, chin-elevate maneuver to start with, and then give the second breath. Be careful not to give way too a lot of breaths or to breathe with way too much drive.
- Following the two breaths, straight away start out the up coming cycle of compressions and breaths. Notice: If there are two individuals offered to do CPR on the kid, modify rescuers every single two minutes — or sooner if the rescuer is fatigued — and give a person to two breaths every single fifteen compressions.
- As shortly as an AED is offered, use it and adhere to the prompts. As shortly as an AED is offered, use it and adhere to the prompts. Use pediatric pads for children more mature than four weeks aged and up to age eight. If pediatric pads usually are not offered, use adult pads. Give a person shock, then restart CPR — starting off with chest compressions — for two far more minutes in advance of offering a second shock. If you’re not experienced to use an AED, a 911 operator or a further crisis clinical operator could be capable to give you directions.
Go on right until the kid moves or assistance arrives.
To carry out CPR on a toddler four weeks aged or more mature
Cardiac arrest in babies is ordinarily owing to a deficiency of oxygen, these kinds of as from choking. If you know that the toddler has an airway blockage, carry out to start with help for choking. If you don’t know why the toddler just isn’t respiration, carry out CPR.
1st, examine the scenario. Touch the toddler and enjoy for a reaction, these kinds of as motion. Do not shake the toddler.
If there is certainly no reaction, phone 911 or your local crisis amount, then straight away commence CPR.
Observe the compressions, airway and respiration (C-A-B) method (beneath) for a toddler below age 1 (except newborns, which incorporate babies up to four weeks aged):
If you observed the toddler collapse, get the AED, if a person is offered, in advance of beginning CPR. If a further particular person is offered, have that particular person phone for assistance straight away and get the AED even though you continue to be with the toddler and carry out CPR.
Compressions: Restore blood stream
- Put the toddler on his or her back on a agency, flat floor, these kinds of as a desk or floor.
- Imagine a horizontal line drawn concerning the baby’s nipples. Put two fingers of a person hand just beneath this line, in the heart of the chest.
- Carefully compress the chest about 1.five inches (about four centimeters).
- Count aloud as you press in a fairly immediate rhythm. You should really press at a level of a hundred to a hundred and twenty compressions a moment, just as you would when offering an adult CPR.
Airway: Open the airway
Following thirty compressions, gently tip the head back by lifting the chin with a person hand and pushing down on the forehead with the other hand.
Respiration: Breathe for the toddler
- Go over the baby’s mouth and nose with your mouth.
- Prepare to give two rescue breaths. Use the strength of your cheeks to provide mild puffs of air (instead of deep breaths from your lungs) to slowly breathe into the baby’s mouth a person time, using a person second for the breath. Watch to see if the baby’s chest rises. If it does, give a second rescue breath. If the chest does not rise, repeat the head-tilt, chin-elevate maneuver and then give the second breath.
- If the baby’s chest nevertheless will not rise, continue chest compressions.
- Give two breaths just after every single thirty chest compressions. If two individuals are performing CPR, give a person to two breaths just after every single fifteen chest compressions.
- Go on CPR right until you see symptoms of lifestyle or right until clinical staff arrive.
Could 01, 2021
.
